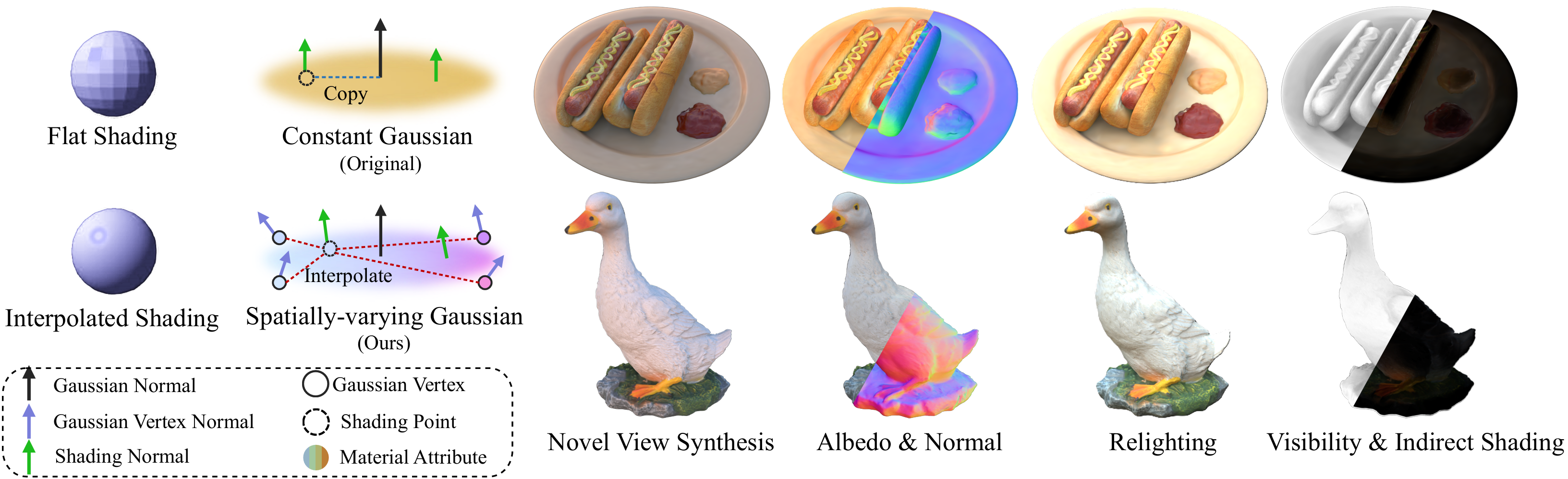
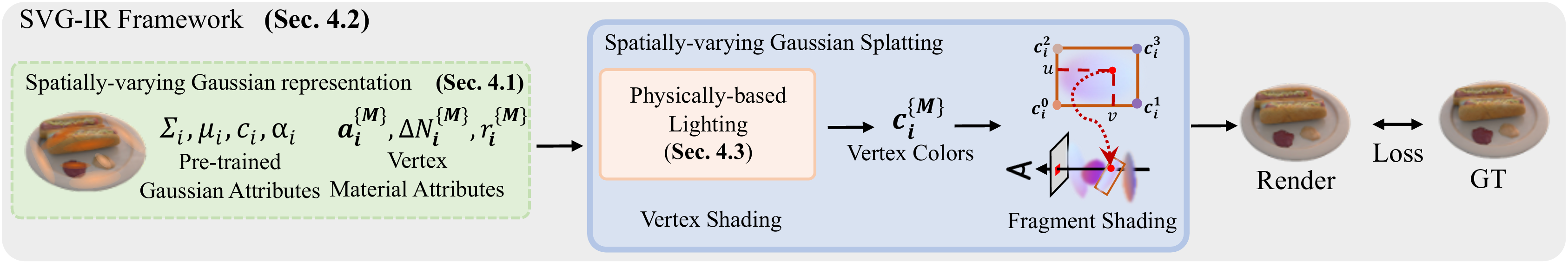
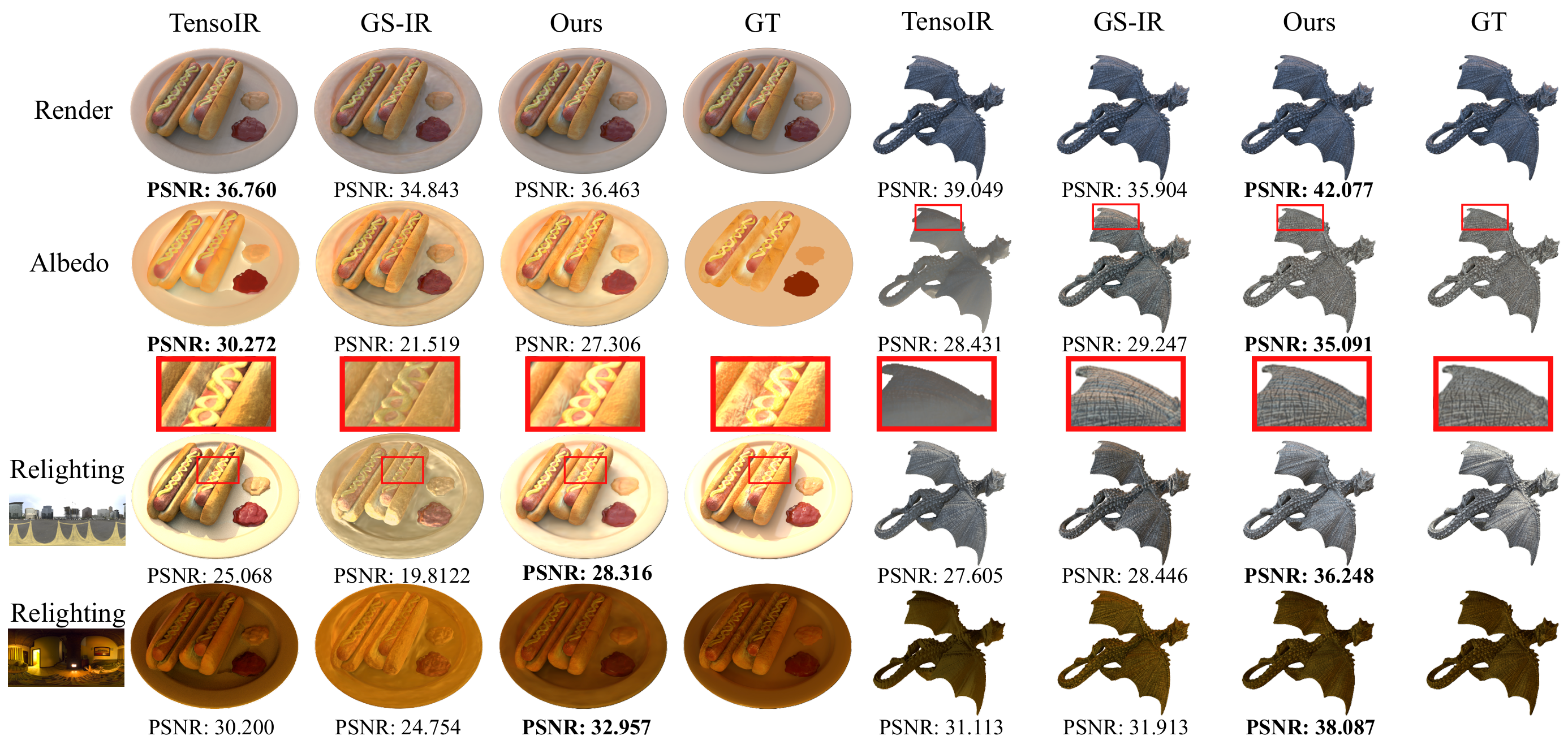
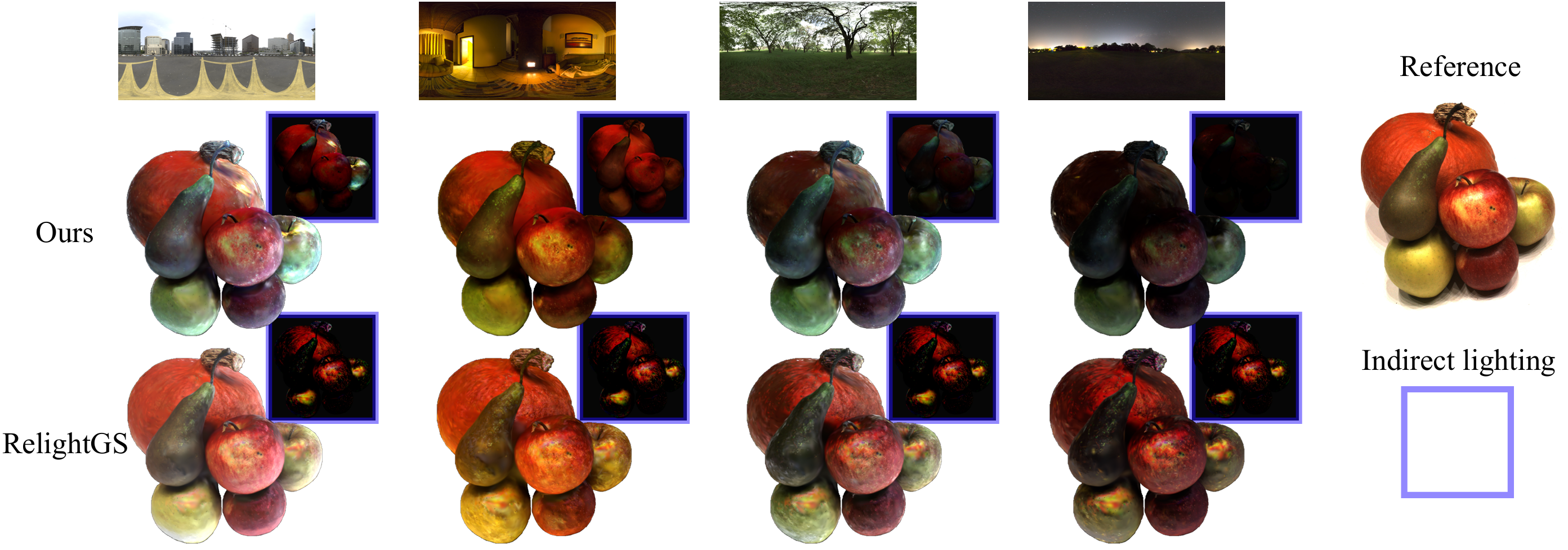
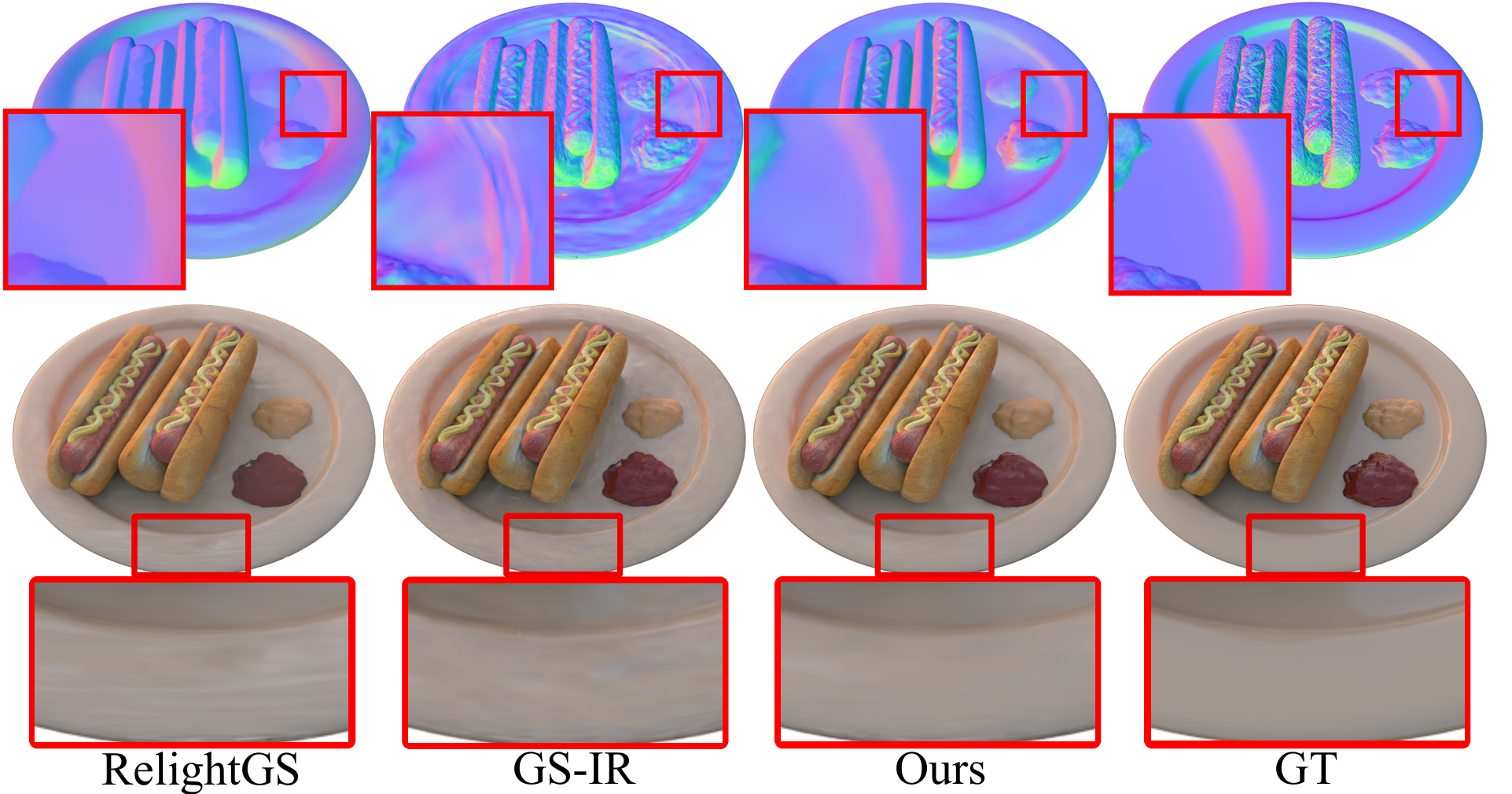
Reconstructing 3D assets from images, known as inverse rendering (IR), remains a challenging task due to its ill-posed nature. 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has demonstrated impressive capabilities for novel view synthesis (NVS) tasks. Methods apply it to relighting by separating radiance into BRDF parameters and lighting, yet produce inferior relighting quality with artifacts and unnatural indirect illumination due to the limited capability of each Gaussian, which has constant material parameters and normal, alongside the absence of physical constraints for indirect lighting. In this paper, we present a novel framework called Spatially-vayring Gaussian Inverse Rendering (SVG-IR), aimed at enhancing both NVS and relighting quality. To this end, we propose a new representation—Spatially-varying Gaussian (SVG)—that allows per-Gaussian spatially varying parameters. This enhanced representation is complemented by a SVG splatting scheme akin to vertex/fragment shading in traditional graphics pipelines. Furthermore, we integrate a physically-based indirect lighting model, enabling more realistic relighting. The proposed SVG-IR framework significantly improves rendering quality, outperforming state-of-the-art NeRF-based methods by 2.5 dB in peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and surpassing existing Gaussian-based techniques by 3.5 dB in relighting tasks, all while maintaining a real-time rendering speed.
@article{
author={Hanxiao Sun and Yupeng Gao and Jin Xie and Jian Yang and Beibei Wang},
title={SVG-IR: Spatially-varying Gaussian Splatting for Inverse Rendering},
year={2025},
journal={Proceedings of CVPR 2025},
}